This is the most common shoulder condition causing pain when lifting the arm.
There are other names used to describe this condition including:
- Rotator cuff tendonitis
- Bursitis
- Supraspinatus (part of the rotator cuff) tendonitis
The most common symptom is pain with movement, although some may experience night pain in the more severe cases.
The pain is often localised to the upper and outer aspect of the shoulder and upper arm and may extend (radiate) to the elbow.
There is often is a sensation of catching when the arm is moved in the horizontal position.
If the condition continues for weeks or months, some may notice greatly with movement and may be incorrectly told that the problem is a frozen shoulder.
The pain occurs because the rotator cuff tendon and bursa (see below) are compressed against bone (the acromion) as the arm is elevated.
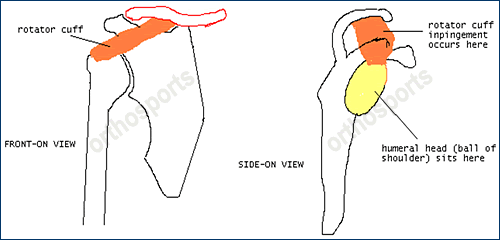
Shoulder Impingement may develop following an injury or as a result of repeated overuse.
In the acute setting, such as fall or lifting a heavy item, there may be an associated tear of the rotator cuff tendon. This may require more comprehensive investigations and treatment.
Shoulder Impingement responds to non-operative treatment in most cases.
Following the correct diagnosis, treatment includes:
- anti-inflammatory and pain relief medications,
- exercises to improve motion and strengthen the shoulder (often with a sports physiotherapist) and,
- avoiding aggravating activities.
If the inflammation continues, injections of cortisone into the subacromial space are required.
If Shoulder Impingement fails to improve, surgery may be required. This is usually arthroscopically depending on the extent of the damage.
An x-ray of the shoulder is usually performed. In more complicated cases other tests such as an arthrogram and MRI scans are required.
Ultrasound examinations are helpful in some cases but are generally less accurate than an MRI scan.
Shoulder Impingement requires prompt and accurate diagnosis and treatment. If this occurs, it is more likely to have a full and uncomplicated recovery.